
V i and v f are the initial and the final velocities of a falling object

Here, we replaced ‘s’ with ‘d’, and ‘d’ is the displacement The fourth equation: d = v i t + 1/2 at 2 ….(4) The third equation: v f 2 = v i 2 + 2* a* d….(3) The free-fall motion formula covers the following equations for a falling body:īelow are the following kinematic equations for deriving the free-fall motion formula:
#Free fall physics calculator free
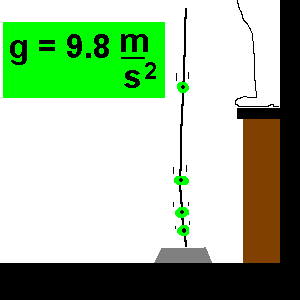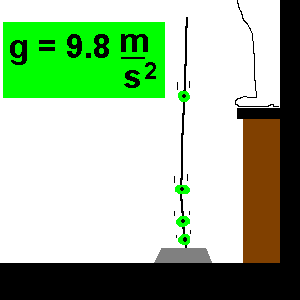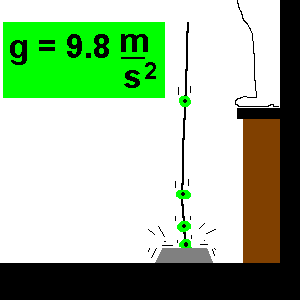
So, the free-fall acceleration formula says that ‘a’ always equals ‘g’ under free fall. We must note that whether the object is falling or rising towards its peak if it is under the sole influence of gravity, its acceleration value will always remain 9.8 ms -2. We know that any object that is moving and being acted upon only by the force of gravity is said to be "in a state of free fall." Such an object experiences a downward acceleration of 9.8 ms -2. So, on this page, we will cover all the equations for a falling body along with the free fall physics formula, and then derive the free fall formula as well. As there is a rate of change of velocity in an object while free-falling, so we can determine the free-fall acceleration formula as well. The eight can be calculated by using the maximum height formula free fall. Since the object falling from a mountain has a maximum height, so does the object. An object possessing a free-fall object formula bears velocity, which we can calculate by using the free-fall velocity formula. As it covers a certain distance, we can describe the free fall distance formula.

Now, because of gravity (g), the body falls in the following manner:įrom this example, we can describe the free-fall motion formula. A free-fall concept that talks about the body freely falling under gravity.Īssume that a body with velocity v is descending freely from a mountain of height (h) for time (t) seconds. A free-falling object formula describes the self-governing phenomena of the body having some mass.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
